What Is Aliasing Define? A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Aliasing In Digital Graphics
Have you ever come across the term "aliasing" and wondered what it really means? If you're into digital graphics, gaming, or video production, understanding aliasing is crucial. Aliasing define refers to the visual distortion that occurs when rendering high-frequency details in digital images or videos. This article will break down everything you need to know about aliasing, its effects, and how to combat it.
Imagine you're playing your favorite video game, and suddenly you notice jagged edges on the edges of objects. That's aliasing at work! These "jagged edges" can ruin the visual experience, making even the most stunning graphics look amateurish. But don't worry; by the end of this article, you'll know exactly how to tackle this issue and enhance your digital content.
This guide is designed to help both beginners and advanced users grasp the concept of aliasing and its implications in various fields. Whether you're a gamer, graphic designer, or video editor, understanding aliasing will take your work to the next level. So, let's dive in!
- The Blackest Man A Journey Into The Darkest Complexions And Their Stories
- Is Josh Gates Married The Truth Behind The Mystery
Understanding Aliasing in Digital Media
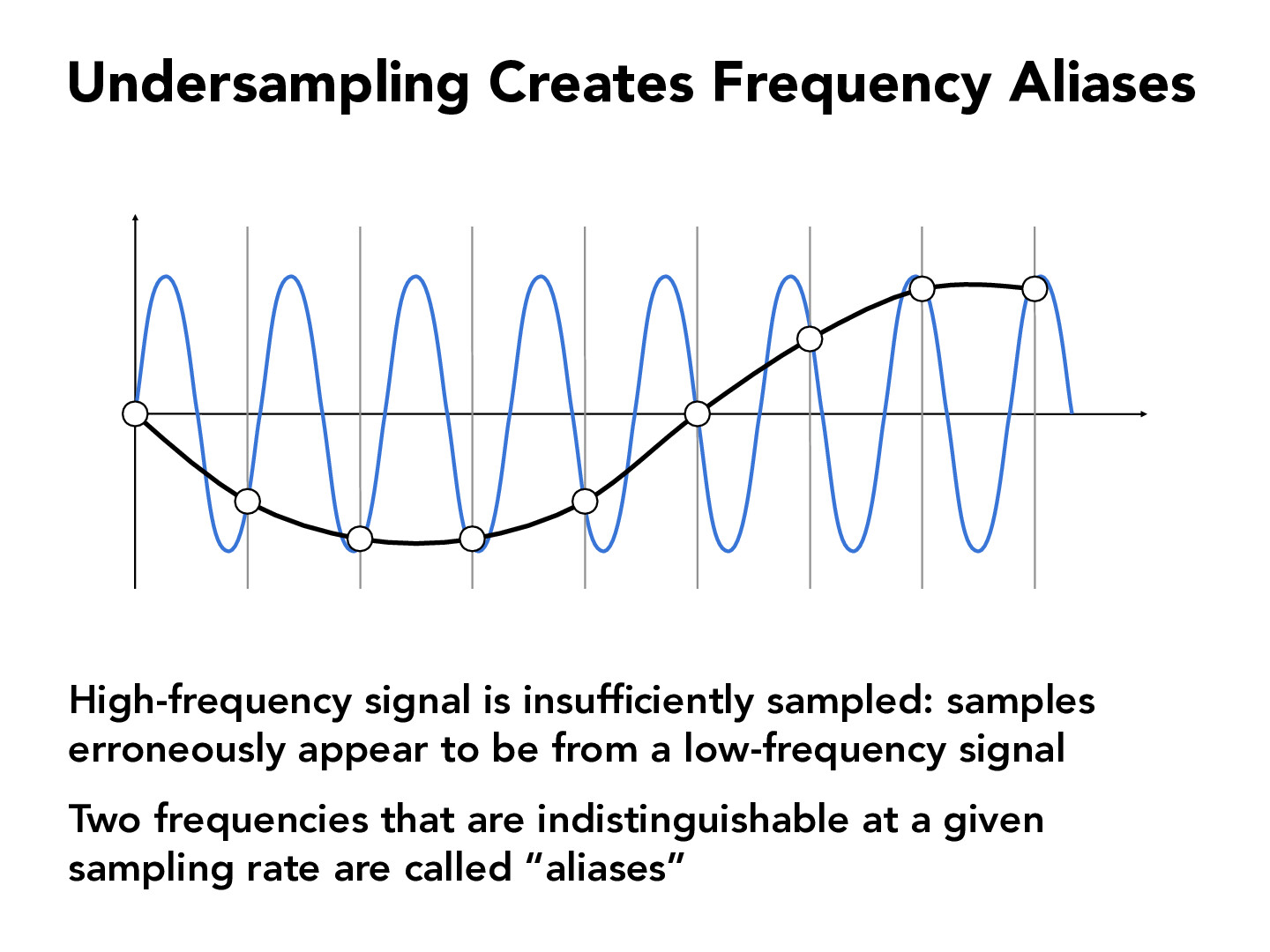
Aliasing define is essentially the distortion that happens when high-frequency signals are sampled at a lower rate than required. In simpler terms, it's like trying to capture a fast-moving object with a camera that doesn't have the speed to keep up. The result? A blurry or jagged representation of the object.
This phenomenon is especially common in digital images, audio, and video. For instance, when you zoom in on a digital photo, you might notice pixelation or stair-step effects along diagonal lines. That's aliasing! It occurs because the digital system can't accurately represent the original analog signal.
How Does Aliasing Affect Digital Graphics?
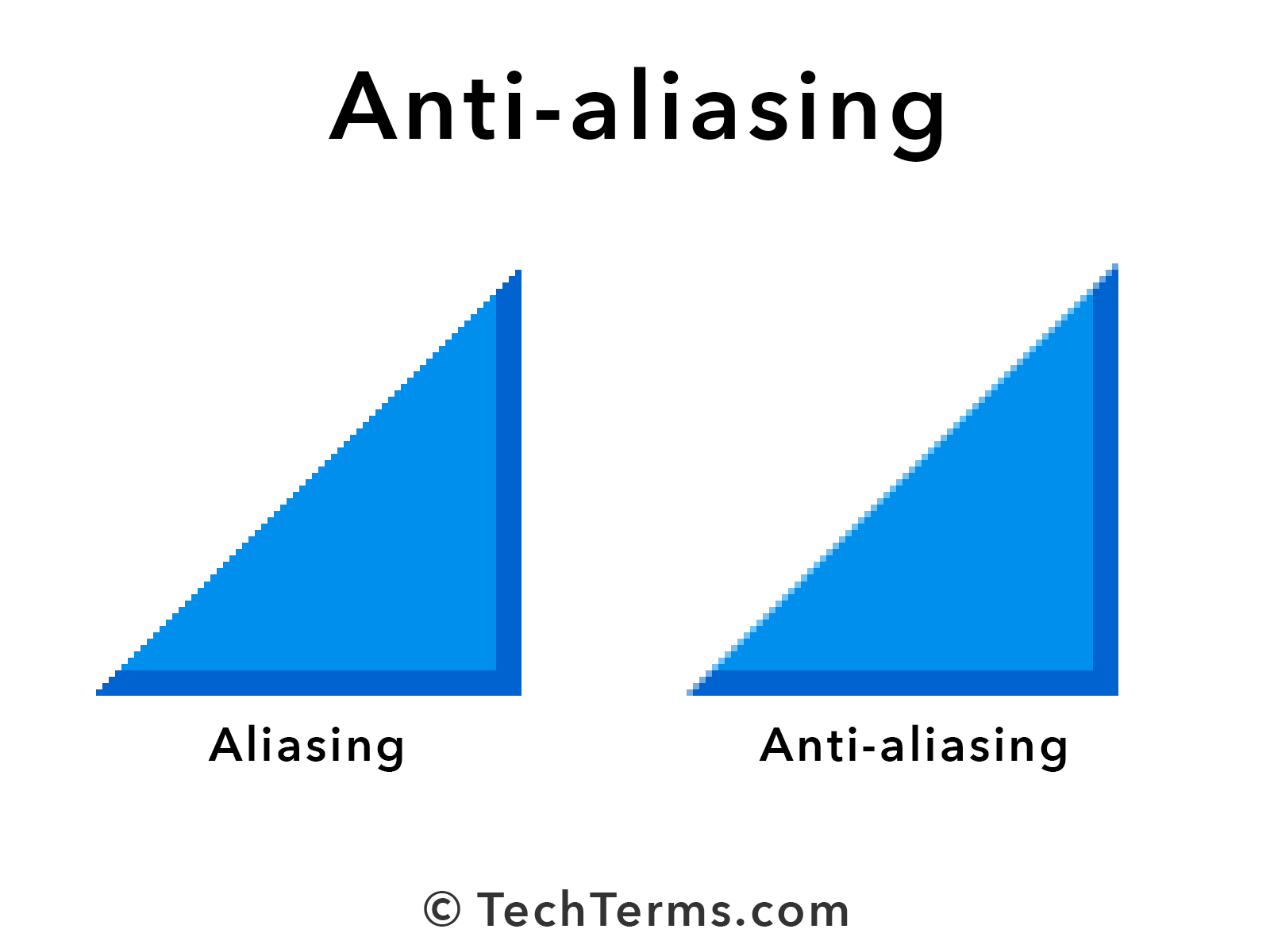
When it comes to digital graphics, aliasing primarily affects the visual quality of images and videos. The most noticeable effect is the jagged edges or "stair-stepping" along diagonal or curved lines. This happens because the digital system tries to approximate continuous lines using discrete pixels.
For example, imagine a diagonal line on a computer screen. Instead of appearing smooth, it might look like a series of tiny steps. This is because each pixel is a square, and the system has to decide which pixels to turn on or off to represent the line. The result? A less-than-perfect representation of the original line.
Common Causes of Aliasing
Aliasing can occur due to several reasons, but the primary cause is insufficient sampling. When a digital system doesn't have enough resolution or processing power to accurately capture high-frequency details, aliasing becomes inevitable.
- Insufficient Resolution: Low-resolution images or displays can't accurately represent fine details.
- Fast-Moving Objects: In videos, fast-moving objects can create blurring or distortion if the frame rate isn't high enough.
- High-Frequency Signals: Audio signals with frequencies above the Nyquist limit can cause aliasing in sound recordings.
Think of it like trying to record a bird's wings flapping at high speed with a slow-motion camera. If the camera isn't fast enough, the wings might appear to move backward or in strange patterns. That's aliasing in action!
Types of Aliasing
There are different types of aliasing, each affecting various aspects of digital media. Let's break them down:
- Geometric Aliasing: This type affects the visual representation of shapes and lines in digital graphics.
- Temporal Aliasing: Occurs in videos when fast-moving objects create distortion due to insufficient frame rates.
- Audio Aliasing: Happens when high-frequency sounds are recorded at a sampling rate that's too low, causing distortion in audio playback.
Each type of aliasing requires a different approach to mitigate its effects. For example, geometric aliasing can be reduced by increasing the resolution or using anti-aliasing techniques, while temporal aliasing requires higher frame rates.
Solutions to Combat Aliasing
Fortunately, there are several methods to reduce or eliminate aliasing in digital media. Here are some of the most effective solutions:
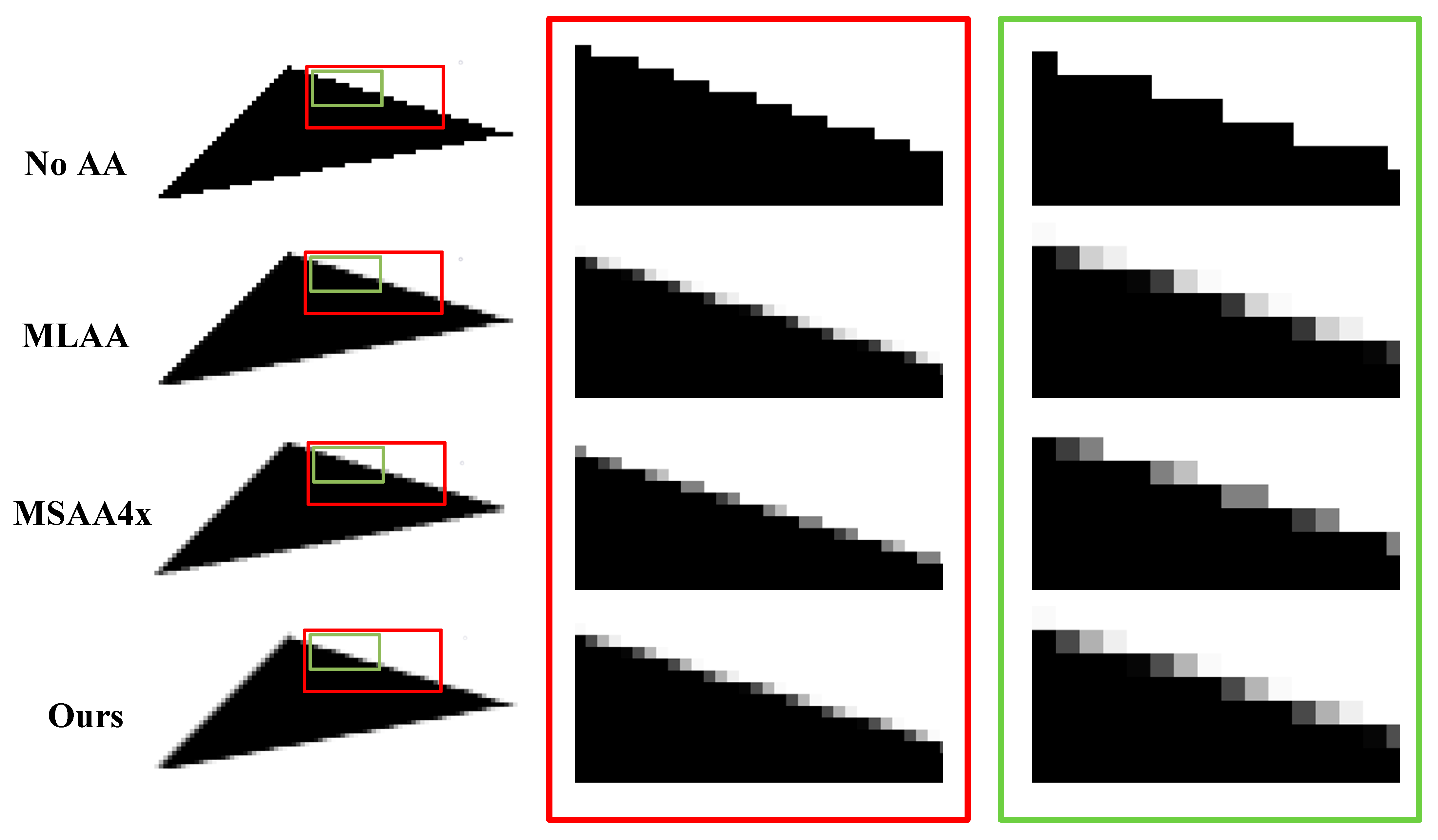
Anti-Aliasing Techniques
Anti-aliasing is a popular method used to smooth out jagged edges in digital graphics. It works by blending the colors of adjacent pixels to create a more natural transition between them.
- Supersampling Anti-Aliasing (SSAA): This technique involves rendering the image at a higher resolution and then downscaling it to the desired size. While effective, it can be resource-intensive.
- Multi-Sample Anti-Aliasing (MSAA): A more efficient alternative to SSAA, MSAA focuses on smoothing out edges without affecting the entire image.
- Fast Approximate Anti-Aliasing (FXAA): A lightweight solution that uses a shader to smooth out edges quickly, making it ideal for real-time applications like gaming.
Choosing the right anti-aliasing technique depends on factors like performance requirements and available resources. For instance, gamers might prefer FXAA for its speed, while professional designers might opt for SSAA for its accuracy.
Improving Resolution and Sampling Rates
Increasing the resolution of images or the sampling rate of audio can significantly reduce aliasing. Higher resolutions allow for more detailed representations of shapes and lines, while higher sampling rates capture more accurate audio signals.
However, this approach comes with its own challenges. Higher resolutions and sampling rates require more processing power and storage space, which can be a limitation for some systems. Therefore, it's essential to strike a balance between quality and performance.
Aliasing in Audio Production
While aliasing is most commonly associated with digital graphics, it also plays a significant role in audio production. Audio aliasing occurs when high-frequency sounds are recorded at a sampling rate that's too low, causing distortion in the playback.
The Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem states that to accurately capture a signal, the sampling rate must be at least twice the highest frequency present in the signal. If this rule isn't followed, aliasing becomes unavoidable.
Preventing Audio Aliasing
To prevent audio aliasing, producers often use anti-aliasing filters before recording. These filters remove high-frequency components that could cause distortion during the sampling process.
Additionally, using higher sampling rates, such as 48 kHz or 96 kHz, can help minimize aliasing effects. While this requires more storage space and processing power, it ensures a more accurate representation of the original audio signal.
Real-World Applications of Aliasing Define
Aliasing isn't just a theoretical concept; it has real-world implications in various fields. Here are some examples:
Gaming Industry
In the gaming industry, aliasing can significantly impact the player experience. Jagged edges or blurring in fast-paced games can disrupt immersion and make the gameplay feel less polished. That's why game developers invest heavily in anti-aliasing techniques to ensure smooth and visually appealing graphics.
Film and Video Production
Aliasing is also a concern in film and video production. High-speed cameras and digital sensors can introduce aliasing artifacts if not properly calibrated. To combat this, filmmakers use techniques like optical low-pass filters and higher frame rates to capture crisp, distortion-free footage.
Medical Imaging
In medical imaging, aliasing can lead to misdiagnosis if high-frequency details aren't accurately represented. For instance, in MRI or CT scans, aliasing can cause artifacts that might be mistaken for actual anatomical features. To avoid this, medical imaging systems employ advanced anti-aliasing techniques and high-resolution sensors.
Tools and Software for Aliasing Mitigation
Several tools and software are available to help mitigate aliasing in digital media. Here are some popular options:
Graphics Software
Professional graphics software like Adobe Photoshop and Blender offer built-in anti-aliasing features. These tools allow users to apply anti-aliasing effects to their designs, ensuring smooth and polished visuals.
Game Engines
Game engines like Unity and Unreal Engine provide developers with a range of anti-aliasing options. From MSAA to FXAA, these engines give developers the flexibility to choose the best solution for their projects.
Audio Editing Software
Audio editing software like Audacity and Pro Tools include anti-aliasing filters to ensure clean and distortion-free recordings. These tools are essential for audio professionals who demand the highest quality in their work.
Future Trends in Aliasing Mitigation
As technology continues to evolve, new methods for mitigating aliasing are emerging. Machine learning and artificial intelligence are being explored as potential solutions to enhance anti-aliasing techniques.
For instance, AI-powered algorithms can analyze digital images and videos to identify and smooth out aliasing artifacts automatically. These algorithms can learn from vast datasets to improve their accuracy over time, making them an exciting prospect for the future of digital media.
AI and Machine Learning in Anti-Aliasing
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing the field of anti-aliasing. By analyzing patterns in digital media, these technologies can predict and correct aliasing artifacts with unprecedented accuracy.
While still in its early stages, AI-powered anti-aliasing has the potential to transform industries like gaming, film, and medical imaging. As these technologies mature, we can expect even smoother and more realistic digital experiences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding aliasing define is crucial for anyone working in digital media. Whether you're a gamer, graphic designer, or audio engineer, aliasing can significantly impact the quality of your work. By employing anti-aliasing techniques and using the right tools, you can minimize aliasing effects and create stunning, distortion-free content.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with aliasing in the comments below. Have you encountered aliasing in your work? How did you tackle it? And don't forget to explore our other articles for more insights into the world of digital media.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Aliasing in Digital Media
- Common Causes of Aliasing
- Types of Aliasing
- Solutions to Combat Aliasing
- Aliasing in Audio Production
- Real-World Applications of Aliasing Define
- Tools and Software for Aliasing Mitigation
- Future Trends in Aliasing Mitigation
- AI and Machine Learning in Anti-Aliasing
- Conclusion
- Johnny Carson Children The Untold Story Behind The Legendary Tv Icons Family Life
- Was Stacie Zabka In Cobra Kai Unveiling The Truth Behind The Iconic Character
Understanding AntiAliasing A Comprehensive Guide
CS184/284A Lecture 3 Antialiasing
AntiAliasing Definition