Audio Aliasing: The Sneaky Distortion Ruining Your Sound
Ever wondered why some audio recordings sound off or distorted, even when everything seems set up perfectly? Well, my friend, let's dive into the world of audio aliasing, the silent culprit behind those annoying glitches. If you're into producing music, recording podcasts, or simply fascinated by how sound works, this is one topic you don't want to miss. Trust me, understanding audio aliasing could save your next project from disaster.
Audio aliasing isn’t something you hear about every day unless you’re deep into audio engineering or digital signal processing. But don’t let the fancy name scare you. It’s actually quite simple once you get the hang of it. Think of it like a glitch in the system that sneaks in when you’re converting analog sound waves into digital ones. And guess what? It can make your audio sound like a robot having a bad day.
Now, before we dive deeper, let’s set the stage. In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about audio aliasing, from what it is and how it happens to ways you can prevent it. So, buckle up, because we’re about to unravel the mysteries of this digital distortion and help you create cleaner, more professional-sounding audio.
- Did Gabriel Iglesias Cheat On His Wife The Truth Behind The Laughter
- Kniko Howard Age Unveiling The Life And Legacy Of A Remarkable Woman
What Exactly is Audio Aliasing?
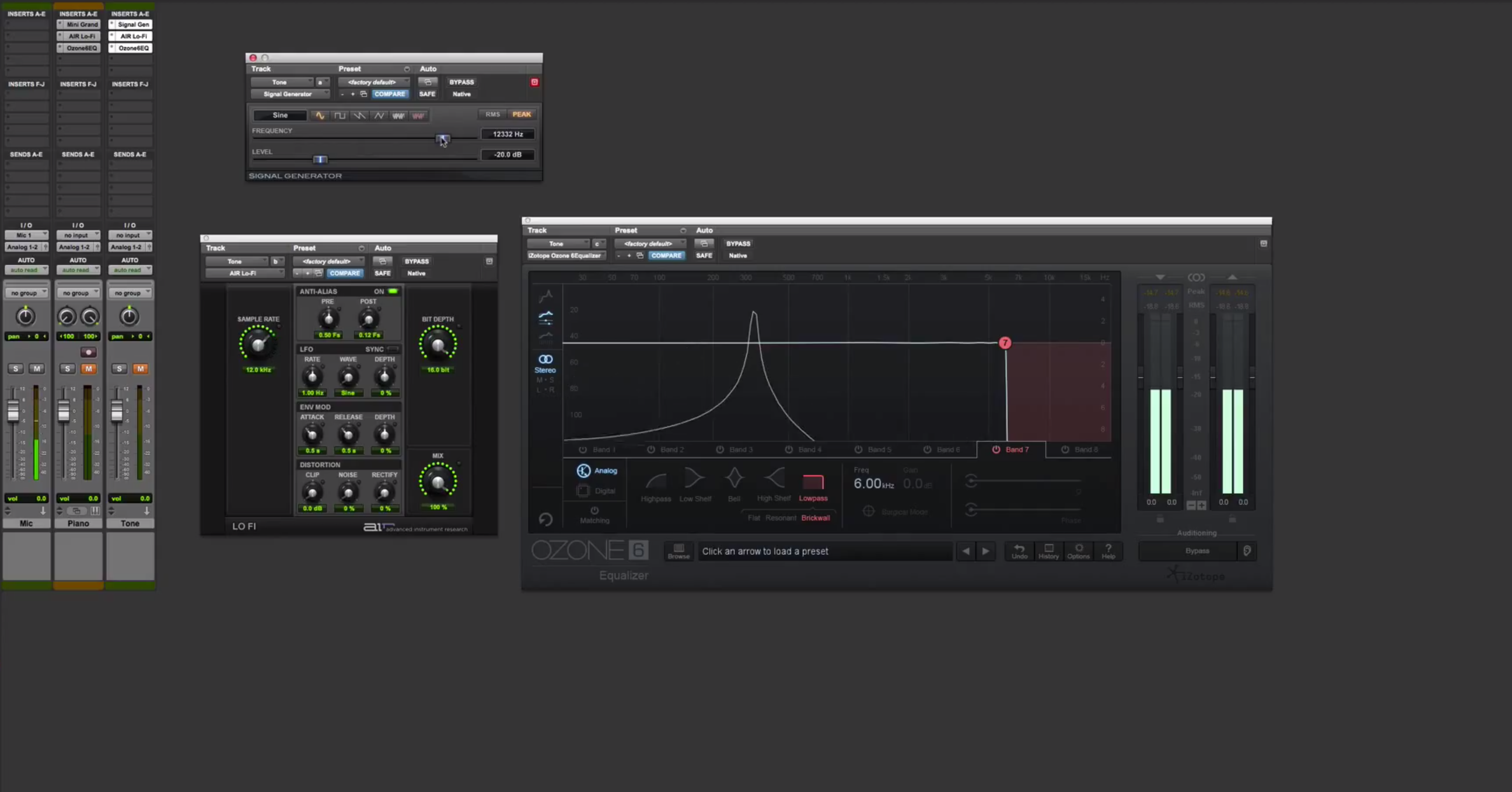
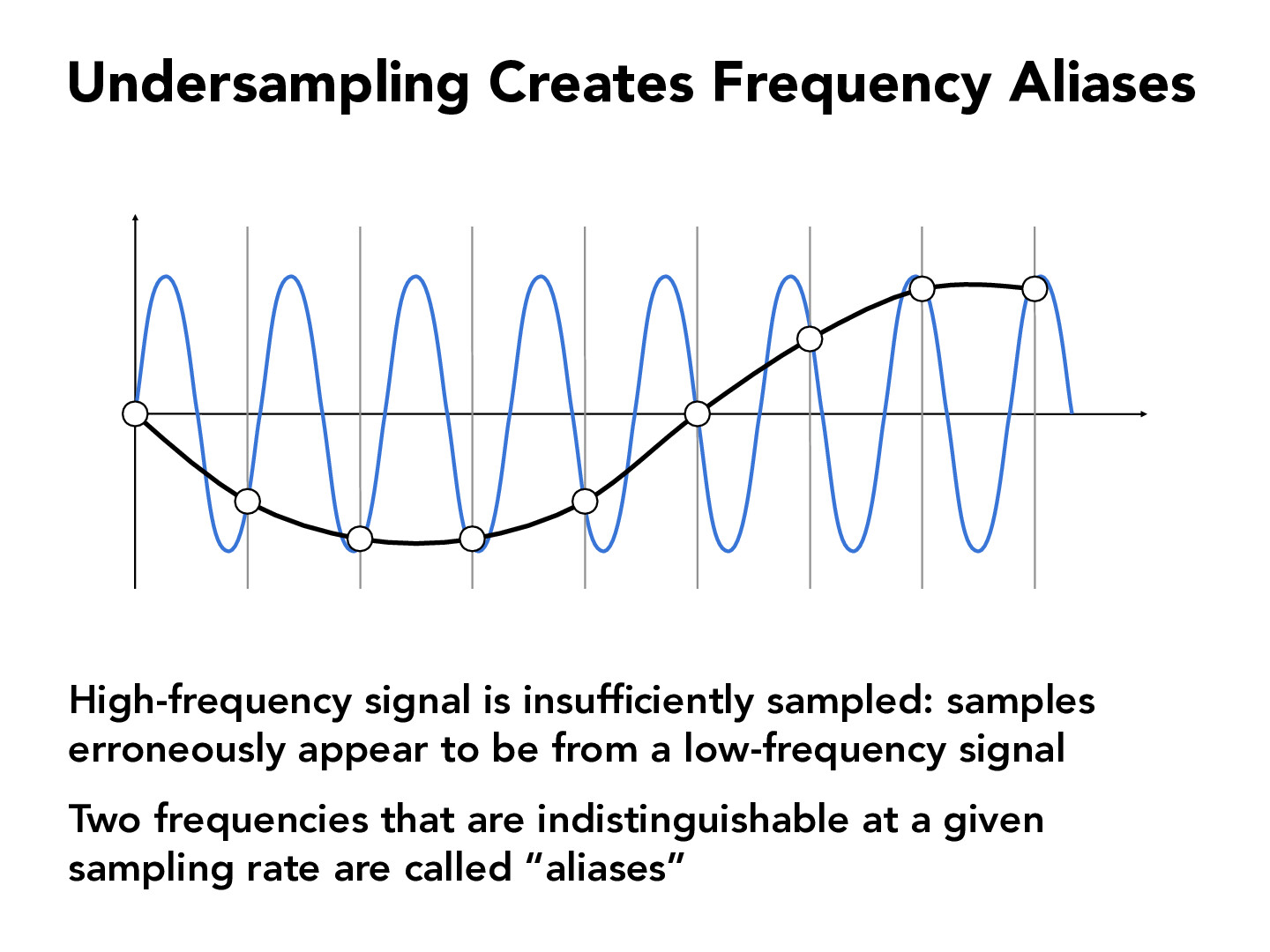
Audio aliasing occurs when a digital system tries to represent an analog signal but fails to capture all the details accurately. Imagine trying to sketch a fast-moving object with only a few quick strokes. You might get the general idea, but the finer details are lost. That’s essentially what happens in the digital world when the sampling rate isn’t high enough to capture all the nuances of an analog sound wave.
The result? Distorted audio that sounds, well, weird. Instead of hearing smooth, natural sound waves, you end up with jagged, unnatural artifacts that can ruin the listening experience. And let’s face it, nobody wants their music or podcast to sound like a broken record.
How Does Aliasing Happen?
Here’s the deal: when you record audio digitally, the system takes snapshots of the sound wave at regular intervals. These snapshots are called samples, and the rate at which they’re taken is known as the sampling rate. If the sampling rate is too low, the system can’t keep up with the rapid changes in the analog signal, leading to aliasing.
- Is Enrica Cenzatti Still Alive Unveiling The Truth About This Iconic Figure
- Content Marketing Vs Advertising Which One Should You Choose For Your Business
Think of it like watching a spinning wheel in a movie. If the frame rate of the camera is too slow, the wheel might appear to spin backward or behave strangely. The same principle applies to audio aliasing. When the sampling rate can’t keep up with the frequency of the sound wave, weird distortions appear.
The Science Behind Audio Aliasing
Let’s get a little nerdy for a moment. According to the Nyquist-Shannon Sampling Theorem, to accurately represent an analog signal in digital form, the sampling rate must be at least twice the highest frequency present in the signal. This is known as the Nyquist frequency. If you go below this threshold, aliasing rears its ugly head.
For example, if you’re recording audio with a sampling rate of 44.1 kHz (the standard for CDs), the highest frequency you can capture without aliasing is 22.05 kHz. Anything above that will get distorted. Makes sense, right? It’s all about keeping up with the speed of the sound waves.
Why Should You Care About Aliasing?
Here’s the kicker: aliasing doesn’t just affect high-frequency sounds. It can seep into your entire audio track, creating unwanted noise and distortion that ruins the overall quality. Whether you’re a musician, podcaster, or audio enthusiast, clean sound is crucial. And aliasing is one of those sneaky problems that can slip under the radar if you’re not paying attention.
Imagine spending hours perfecting a track, only to realize later that it’s littered with aliasing artifacts. Not cool, right? That’s why understanding this phenomenon is so important. By knowing how aliasing works, you can take steps to prevent it and ensure your audio sounds as good as it possibly can.
Common Causes of Audio Aliasing
So, what exactly causes aliasing in the first place? Let’s break it down:
- Low Sampling Rates: As we discussed earlier, if your sampling rate is too low, it can’t capture all the details of the sound wave, leading to aliasing.
- High-Frequency Sounds: Sounds with frequencies above the Nyquist limit are especially prone to aliasing. Think of those sharp, high-pitched tones that can slip through the cracks.
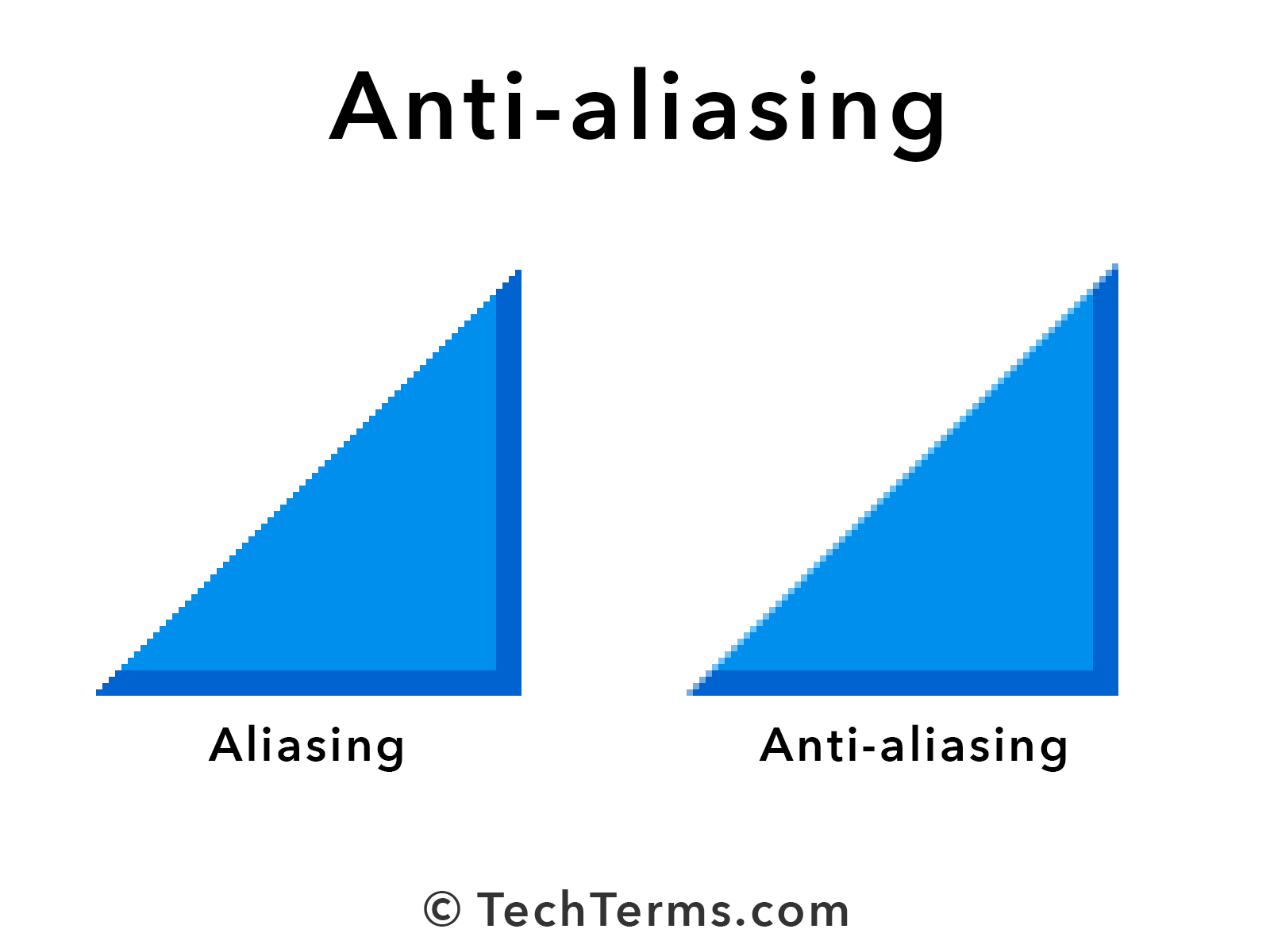
- Poor Anti-Aliasing Filters: Many audio systems use filters to smooth out the signal and prevent aliasing. But if these filters aren’t up to the task, aliasing can still occur.
- Inadequate Equipment: Sometimes, the problem lies in the hardware itself. Cheap or outdated equipment might not have the capabilities to handle high-frequency sounds properly.
Now that we’ve identified the culprits, let’s talk about how to fix them. Stay tuned!
How to Detect Audio Aliasing
Spotting aliasing in your audio can be tricky, especially if you’re not sure what to listen for. Here are a few telltale signs:
- Unnatural Sound: If your audio sounds robotic or distorted, aliasing might be to blame.
- Strange Frequencies: Listen for unexpected tones or pitches that don’t belong in your track. These could be aliasing artifacts.
- Inconsistent Quality: If certain parts of your audio sound clean while others are distorted, aliasing could be the culprit.
One effective way to detect aliasing is to use a spectrum analyzer. This tool lets you visualize the frequencies in your audio and spot any anomalies. It’s like having x-ray vision for sound waves!
Tools for Detecting Aliasing
Here are a few tools you can use to detect aliasing:
- Spectrum Analyzers: These tools provide a visual representation of your audio’s frequency spectrum, making it easier to spot aliasing.
- Audio Editors: Many modern audio editing software programs come with built-in features to help you identify and fix aliasing.
- Test Tones: Generating test tones at different frequencies can help you pinpoint where aliasing might be occurring.
Armed with these tools, you’ll be able to catch aliasing before it ruins your audio.
Preventing Audio Aliasing
The good news is that aliasing is preventable. Here are some tips to keep your audio clean and distortion-free:
- Use High Sampling Rates: Always record at a sampling rate that’s well above the Nyquist frequency. For most applications, 44.1 kHz or higher is a safe bet.
- Invest in Quality Equipment: Good-quality microphones, preamps, and converters can make a huge difference in reducing aliasing.
- Apply Anti-Aliasing Filters: Make sure your audio system has effective anti-aliasing filters in place to smooth out the signal.
- Limit High-Frequency Content: If you’re working with sounds that have a lot of high-frequency content, consider using filters to reduce the risk of aliasing.
By following these steps, you can minimize the chances of aliasing creeping into your audio projects.
Best Practices for Clean Audio
Here are a few additional best practices to ensure your audio stays aliasing-free:
- Monitor Regularly: Keep an ear out for any signs of distortion or unnatural sound during the recording and editing process.
- Use Quality Software: Choose audio editing software that’s designed to handle high-frequency sounds effectively.
- Stay Updated: Keep your equipment and software up to date to take advantage of the latest advancements in anti-aliasing technology.
With these strategies in place, you’ll be well on your way to producing professional-quality audio.
Real-World Examples of Audio Aliasing
To better understand aliasing, let’s look at a few real-world examples:
- Music Production: In electronic music, aliasing can occur when synthesizers or digital effects processors fail to capture the nuances of high-frequency sounds.
- Podcasting: Podcasters often encounter aliasing when recording interviews or live events, especially if they’re using low-quality equipment.
- Video Game Audio: In video games, aliasing can affect sound effects and music, leading to an overall decrease in audio quality.
These examples highlight just how widespread aliasing can be and why it’s so important to address it in any audio-related project.
Case Study: Fixing Aliasing in a Music Track
Let’s take a look at a case study where aliasing was successfully addressed in a music track:
A musician was recording a high-energy electronic track filled with sharp, high-pitched synthesizer sounds. During playback, they noticed strange distortions that didn’t match the original composition. After some investigation, they realized the issue was aliasing caused by an insufficient sampling rate.
To fix the problem, they increased the sampling rate to 96 kHz and applied a high-quality anti-aliasing filter. The result? A clean, distortion-free track that captured all the nuances of the original sound.
Advanced Techniques for Eliminating Aliasing
If you’re serious about eliminating aliasing, here are some advanced techniques to consider:
- Oversampling: This involves temporarily increasing the sampling rate during processing to reduce the risk of aliasing.
- Windowing Functions: These mathematical functions can help smooth out the signal and reduce aliasing artifacts.
- Phase Manipulation: Adjusting the phase of the audio signal can sometimes help mitigate aliasing effects.
While these techniques require a deeper understanding of digital signal processing, they can be incredibly effective in certain situations.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you’re struggling to eliminate aliasing on your own, it might be time to seek professional help. Audio engineers and digital signal processing experts have the skills and tools to tackle even the toughest aliasing problems. Don’t be afraid to reach out for assistance if you need it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, audio aliasing might seem like a small issue, but it can have a big impact on the quality of your audio projects. By understanding what causes aliasing and how to prevent it, you can ensure your recordings sound as good as they possibly can.
Remember, clean audio is key to producing professional-sounding music, podcasts, and other audio content. So, take the time to learn about aliasing and implement the strategies we’ve discussed. Your listeners will thank you for it!
And hey, if you found this article helpful, why not share it with your friends and fellow audio enthusiasts? Or leave a comment below with your thoughts and questions. Let’s keep the conversation going!
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is Audio Aliasing?
- The Science Behind Audio Aliasing
- Common Causes of Audio Aliasing
- How to Detect Audio Aliasing
- Preventing Audio Aliasing
- Real-World Examples of Audio Aliasing
- Advanced Techniques for Eliminating Aliasing
- Conclusion
- Unstoppable The Jawdropping Net Worth Of Chuck Norris
- Is Josh Gates Married The Truth Behind The Mystery
Digital Audio 101 What is Aliasing? — Pro Audio Files
CS184/284A Lecture 3 Antialiasing
AntiAliasing Definition