What Is Aliasing? The Ultimate Guide To Understanding Aliasing In Digital Media
Imagine this scenario: you're watching your favorite movie, and suddenly you notice jagged edges on characters or weird pixelated patterns when objects move fast. Ever wondered what that's all about? Well, my friend, that's aliasing in action. Let's dive deep into what aliasing really is, why it happens, and how we can fix it.
Aliasing is one of those terms that gets thrown around a lot in the tech world, especially when talking about graphics, audio, and video. But what does it mean exactly? In simple terms, aliasing occurs when a digital system tries to represent a continuous signal, like an image or sound wave, but ends up distorting it due to limitations in resolution or sampling rate. Think of it as trying to fit a square peg into a round hole—it just doesn't work out perfectly.
Now, before we get into the nitty-gritty details, let me tell you why this topic matters. Whether you're a gamer, a filmmaker, or just someone who enjoys high-quality visuals, understanding aliasing can help you appreciate the technology behind your favorite media. Plus, knowing how to avoid aliasing can make a huge difference in the quality of your digital experiences. So, buckle up, because we're about to take a journey through the fascinating world of aliasing!
- Fluffy Divorced The Ultimate Guide To Understanding And Navigating Life After Divorce
- Shane Gillis Girlfriend Grace The Inside Story You Need To Know
Understanding Aliasing in Digital Media
What Causes Aliasing?
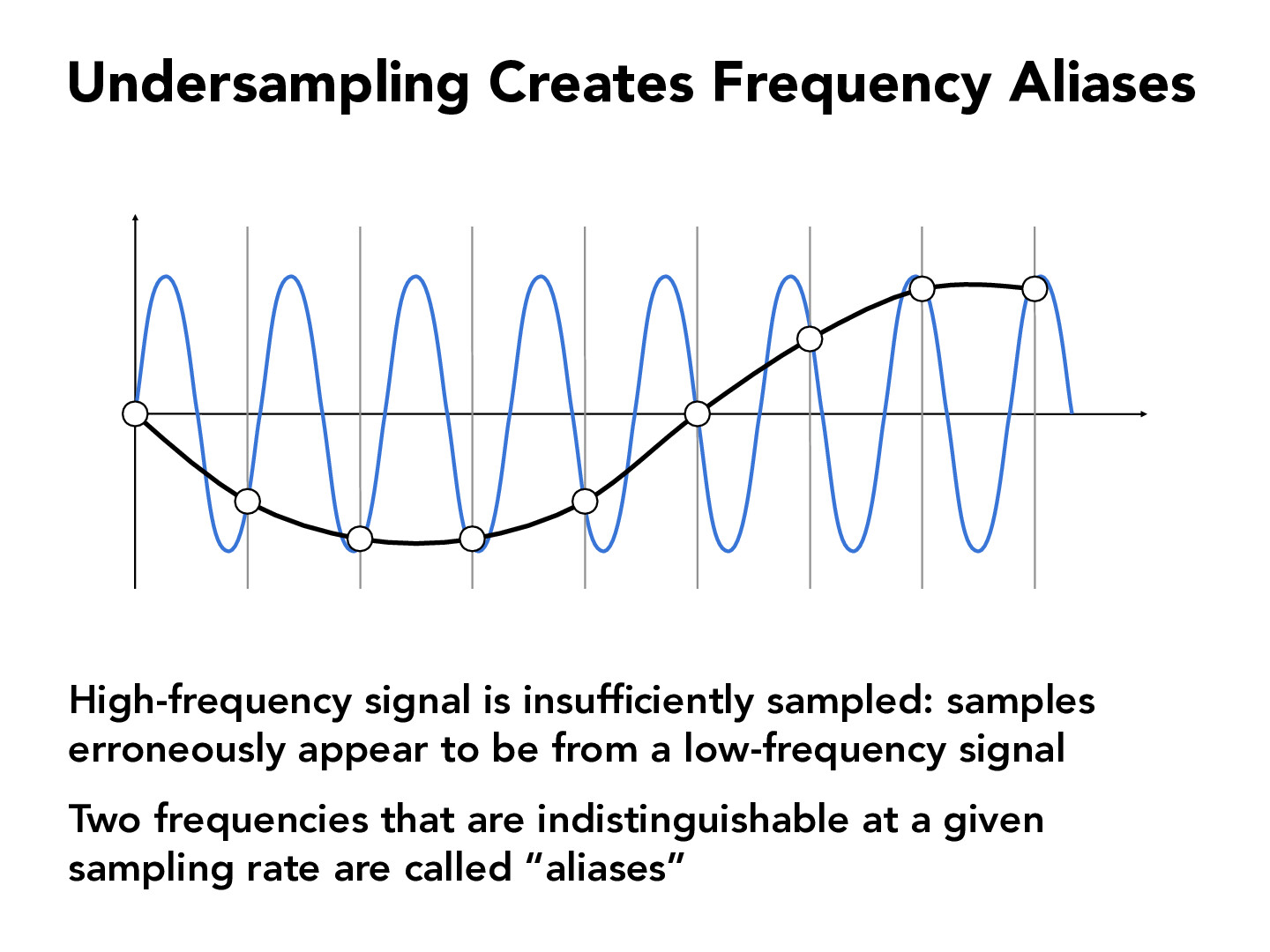
Alright, so let's break it down. Aliasing happens when a system samples a signal at a rate lower than what's required to accurately represent it. For example, if you're recording a sound wave with a frequency higher than half the sampling rate, you'll end up with a distorted version of the original signal. This principle is based on something called the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem, which states that you need to sample a signal at least twice its highest frequency to avoid distortion.
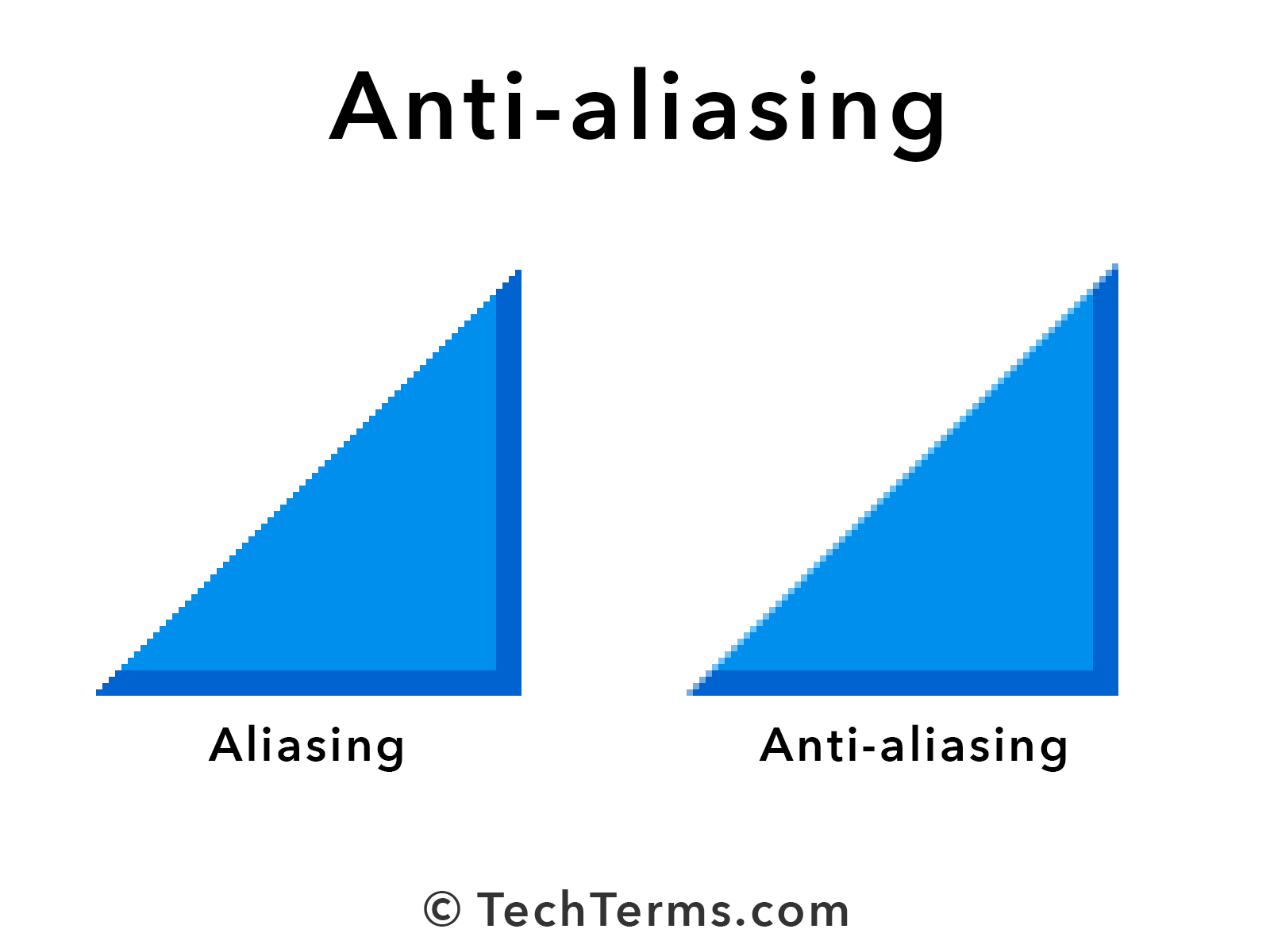
In the world of visuals, aliasing shows up as jagged edges, also known as "jaggies," or unwanted patterns called Moiré effects. These issues occur because the digital representation of an image doesn't have enough resolution to smoothly render curves or diagonal lines. It's like looking at a staircase instead of a smooth slope.
Types of Aliasing
There are different types of aliasing depending on the context. In graphics, we often talk about spatial aliasing, which refers to the visual artifacts in images or videos. On the other hand, temporal aliasing affects motion, causing objects to appear to move strangely or flicker. Audio aliasing, meanwhile, results in unwanted noise or distortion in sound recordings.
- Taylor Fritz Married The Inside Scoop You Didnrsquot Know You Needed
- Damon Wayans And Lisa Wayans A Family Dynasty In Comedy
- Spatial Aliasing: Jagged edges and pixelation in images.
- Temporal Aliasing: Stuttering or flickering in animations or video playback.
- Audio Aliasing: Distortion in sound caused by improper sampling rates.
How Aliasing Affects Your Digital Experience
When aliasing rears its ugly head, it can ruin the immersion in games, movies, or even photos. For instance, in gaming, aliasing can make characters look blocky or unrealistic, breaking the illusion of a seamless virtual world. In video production, it can cause distracting patterns that take away from the story being told. And in audio, aliasing can introduce noise that makes music or dialogue sound off.
But here's the thing: aliasing isn't just a problem for professionals. Even casual users can encounter it when viewing low-quality content or using outdated hardware. That's why understanding aliasing is crucial for anyone who wants to enjoy their digital content without compromise.
The Impact of Aliasing in Gaming
Gamers, listen up! Aliasing can make or break your gaming experience. Imagine playing a first-person shooter where the edges of walls and characters look like they're made of Lego bricks. Not exactly the immersive experience you're looking for, right? That's why modern games use techniques like anti-aliasing to smooth out those jagged edges and create a more realistic environment.
Aliasing in Video Production
For filmmakers and video editors, aliasing can be a major headache. It often shows up as Moiré patterns in footage, especially when shooting detailed textures like clothing or architecture. To combat this, videographers use filters and post-processing techniques to minimize aliasing and ensure their final product looks polished and professional.
Anti-Aliasing Techniques: Your Weapon Against Aliasing
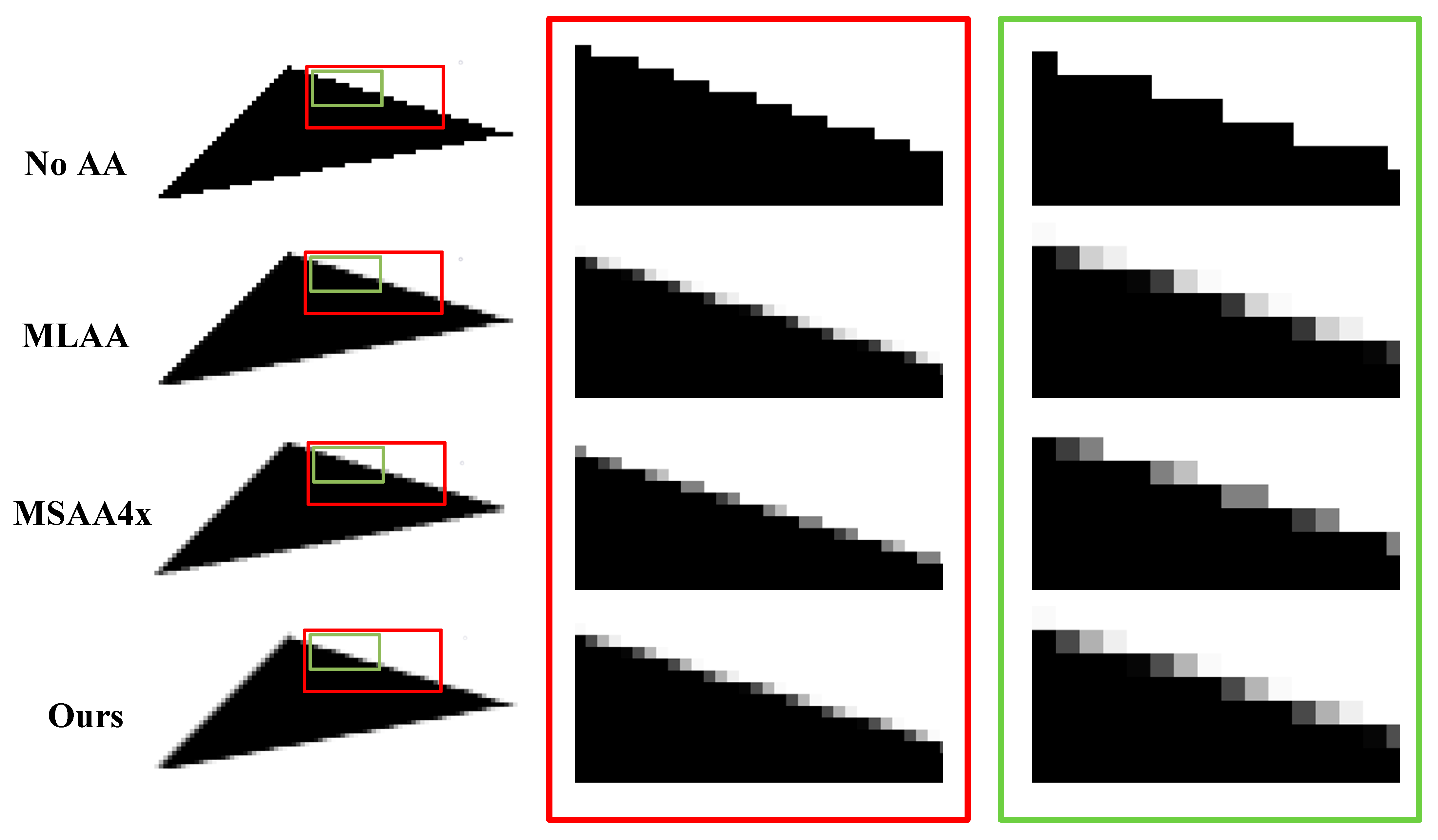
Luckily, there are ways to fight back against aliasing. One of the most common methods is anti-aliasing, which involves smoothing out jagged edges by blending colors along the boundaries of objects. There are several types of anti-aliasing techniques, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Types of Anti-Aliasing
- Supersampling Anti-Aliasing (SSAA): Renders the image at a higher resolution and then downsamples it, resulting in smoother edges. However, it can be resource-intensive.
- Multi-Sample Anti-Aliasing (MSAA): A more efficient version of SSAA that focuses on sampling only the edges of objects, reducing performance impact.
- Fast Approximate Anti-Aliasing (FXAA): A lightweight solution that applies a blur effect to smooth out edges quickly, but may sacrifice some detail.
Real-World Examples of Aliasing
To better understand aliasing, let's look at some real-world examples. In photography, aliasing can occur when capturing fine details like fabric textures or repetitive patterns. This is why many cameras have anti-aliasing filters built-in to reduce the risk of Moiré effects.
In the music industry, aliasing can be a problem when converting analog audio to digital formats. If the sampling rate isn't high enough, it can lead to unwanted artifacts in the sound. That's why professional audio equipment often uses oversampling techniques to minimize aliasing.
Aliasing in Action: A Case Study
Take, for example, the classic video game "Minecraft." Due to its blocky nature, aliasing isn't as noticeable in this game. However, when players zoom in on distant landscapes, the edges of blocks can become jagged and pixelated. To address this, the game developers implemented anti-aliasing techniques to improve the visual experience.
How Technology is Tackling Aliasing
As technology advances, new solutions for combating aliasing are emerging. Modern GPUs are becoming more powerful, allowing for more sophisticated anti-aliasing techniques without sacrificing performance. Additionally, machine learning algorithms are being developed to predict and correct aliasing in real-time, opening up exciting possibilities for the future of digital media.
Future Trends in Anti-Aliasing
One promising development is the use of deep learning to enhance anti-aliasing. By training neural networks on large datasets of high-quality images, researchers are creating algorithms that can intelligently smooth out edges while preserving important details. This approach could revolutionize how we handle aliasing in everything from gaming to video production.
Conclusion: Embrace the Fight Against Aliasing
In conclusion, aliasing is an important concept to understand if you want to enjoy high-quality digital experiences. Whether you're a gamer, filmmaker, or music enthusiast, knowing how to recognize and combat aliasing can make a big difference in the quality of your content. By using anti-aliasing techniques and staying up-to-date with the latest technology, you can ensure that your digital world remains smooth, sharp, and free from distortion.
So, what are you waiting for? Share this article with your friends, leave a comment below, and let's start a conversation about how we can all fight the good fight against aliasing. Together, we can create a digital future that's clear, crisp, and aliasing-free!
Table of Contents
- Understanding Aliasing in Digital Media
- What Causes Aliasing?
- Types of Aliasing
- How Aliasing Affects Your Digital Experience
- The Impact of Aliasing in Gaming
- Aliasing in Video Production
- Anti-Aliasing Techniques: Your Weapon Against Aliasing
- Real-World Examples of Aliasing
- How Technology is Tackling Aliasing
- Future Trends in Anti-Aliasing
- Is Josh Gates Married The Truth Behind The Mystery
- Eams Insurance Search The Ultimate Guide To Simplify Your Insurance Needs
Understanding AntiAliasing A Comprehensive Guide
CS184/284A Lecture 3 Antialiasing
AntiAliasing Definition