What Is Aliasing Sound And Why You Need To Know About It
Alright folks, let’s dive right into the world of audio production and engineering. If you’ve ever wondered why some recordings sound a little off or why certain frequencies seem distorted, you’re not alone. Today, we’re unraveling the mystery behind aliasing sound. Whether you’re an aspiring musician, a sound engineer, or just someone curious about how audio works, this topic is crucial. So, grab your headphones and let’s get started!
Aliasing sound might sound like some fancy sci-fi term, but it’s actually a pretty common issue in digital audio. In simple terms, aliasing happens when a signal is sampled improperly, causing unwanted frequencies to creep into your recordings. This can ruin the quality of your audio, making it sound less polished and professional. We’ll break this down further as we go along, but trust me, by the end of this article, you’ll be an aliasing expert!
Before we jump into the nitty-gritty, let’s set the stage. If you’ve ever worked with digital audio workstations (DAWs) or played around with audio editing software, you’ve probably encountered aliasing in some form. It’s one of those things that can sneak up on you if you’re not careful. But don’t worry, by the time you finish reading this, you’ll know exactly how to spot it, prevent it, and fix it. Let’s get to it!
- Shayanna Jenkins And Her Sister Relationship Now A Closer Look
- Unveiling The Allure Of Robyn Hilton Sexy Moments
Understanding the Basics of Aliasing Sound
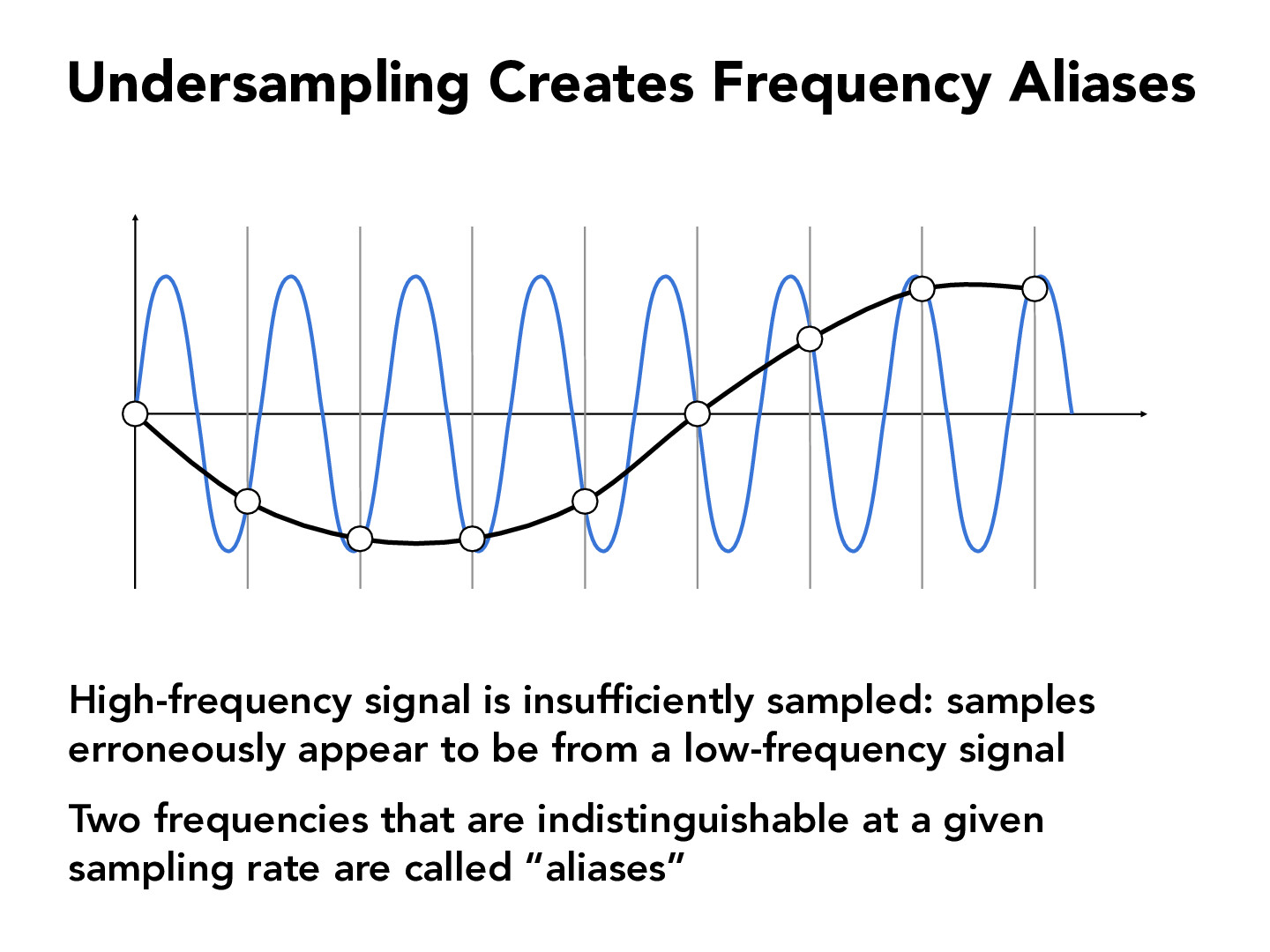
Now that we’ve got your attention, let’s dig deeper into what aliasing sound really is. Picture this: you’re recording a high-pitched sound, and suddenly, instead of hearing that sharp, crisp frequency, you end up with a weird, lower tone that doesn’t belong. That, my friend, is aliasing at work. It’s like when your favorite song gets a little glitchy, and it’s all because of how the sound was processed.
What Causes Aliasing in Audio?
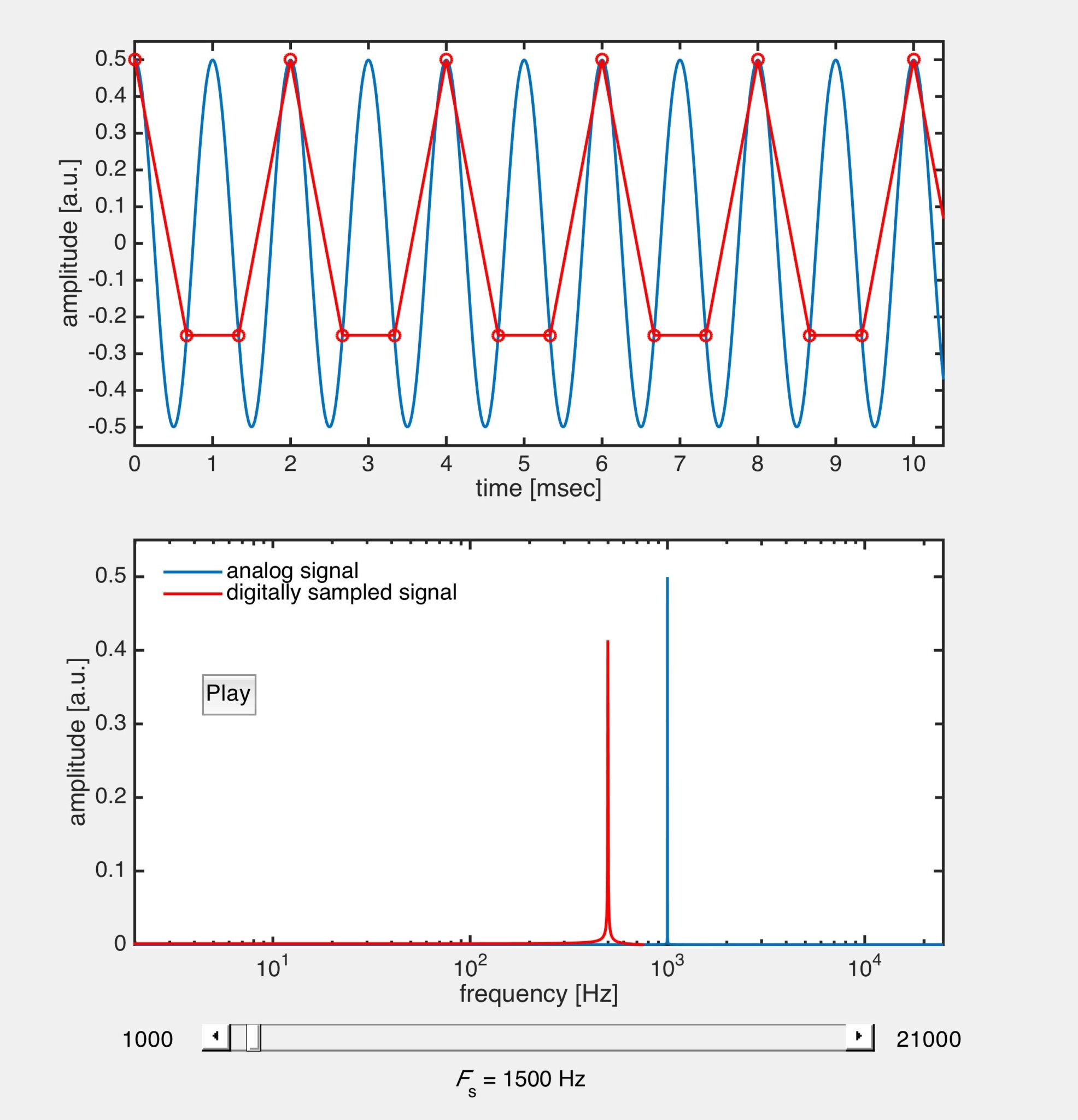
Alright, so what exactly causes aliasing? Here’s the deal: when you’re converting an analog signal into a digital one, the system samples the audio at regular intervals. If the sampling rate isn’t high enough to capture all the nuances of the sound, especially the higher frequencies, those frequencies can get misinterpreted. Instead of hearing the original tone, you end up with a distorted version. It’s like trying to draw a smooth curve with only a few points – it just doesn’t look right.
Let’s break it down further:
- Who Is Gabriel Iglesias Gf The Ultimate Guide To Fluffys Love Life
- Stephanie Mcmahon Net Worth The Untold Story Of Wwes Powerhouse
- Sampling Rate: This is how often the system checks the audio signal. If it’s too low, aliasing can occur.
- High Frequencies: These are the most susceptible to aliasing because they require more samples to be accurately represented.
- Digital Conversion: The process of turning analog sound waves into digital data can sometimes lose information, leading to aliasing.
How Does Aliasing Affect Your Audio?
So, why should you care about aliasing? Well, if you’re producing music, creating podcasts, or even just editing videos, aliasing can ruin the quality of your work. Imagine spending hours perfecting a track, only to find out that some of the frequencies sound off. That’s not just frustrating – it can also cost you professionally. Listeners expect high-quality audio, and aliasing can make your work sound amateurish.
Recognizing Aliasing in Your Recordings
Here’s the tricky part: aliasing isn’t always obvious. Sometimes, it manifests as a subtle distortion that’s hard to pinpoint. Other times, it can be a glaring issue that makes your audio sound completely off. To spot aliasing, listen closely for:
- Unwanted frequencies that don’t belong in your mix.
- Distorted high-pitched sounds that seem out of place.
- Any inconsistency in the audio quality.
Trust your ears – they’re your best tool for detecting aliasing. If something sounds off, it probably is.
Preventing Aliasing Sound
Now that you know what aliasing is and how it affects your audio, let’s talk about prevention. The good news is that aliasing is largely preventable if you take the right steps. Here’s what you can do:
Use a Higher Sampling Rate
One of the simplest ways to prevent aliasing is by using a higher sampling rate. Most modern audio interfaces support sampling rates of 44.1 kHz or higher. By increasing the sampling rate, you give the system more data points to accurately capture the sound. Think of it like taking more photos of a moving object – the more pictures you take, the clearer the motion becomes.
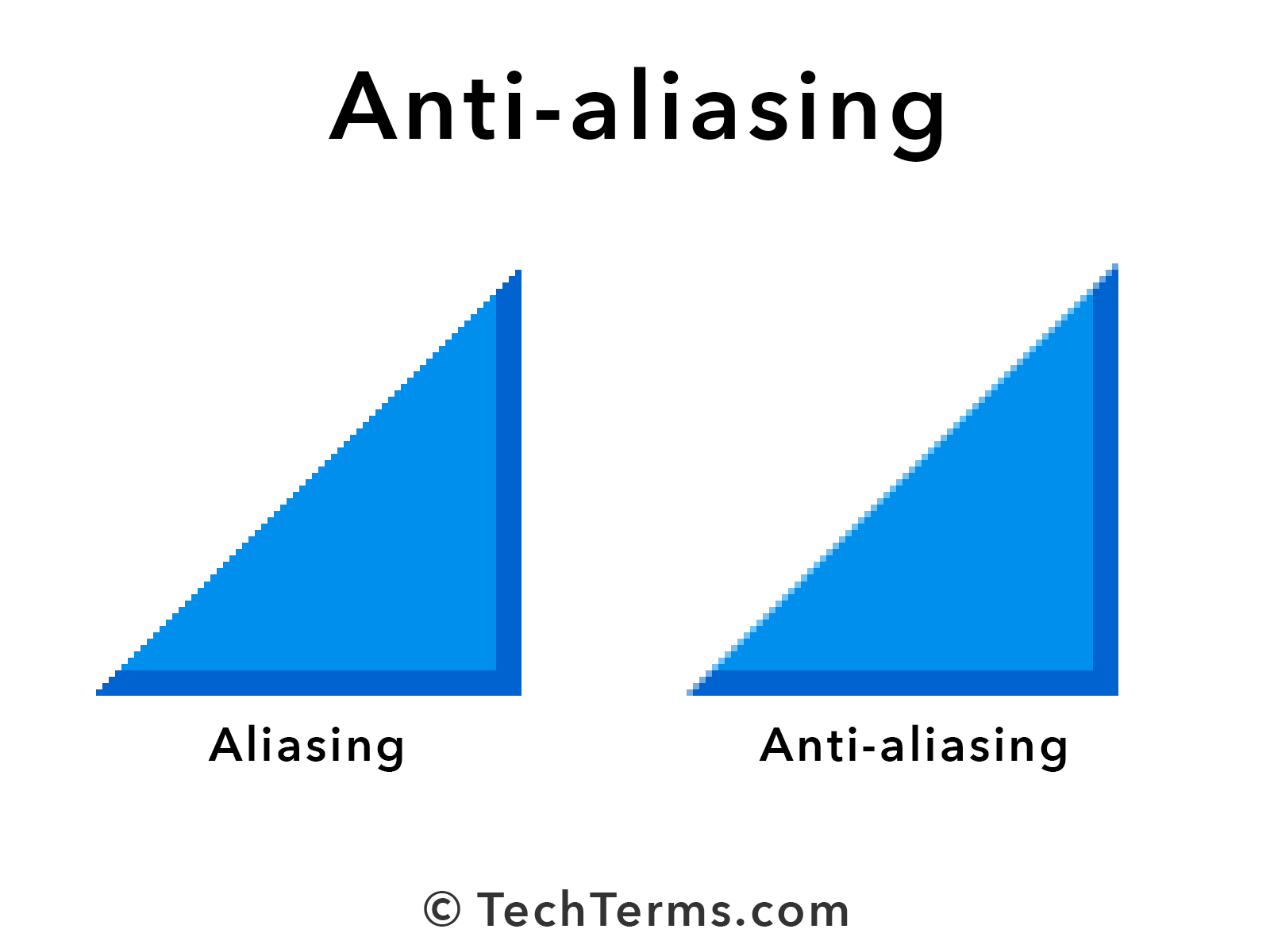
Apply Anti-Aliasing Filters
Another effective method is using anti-aliasing filters. These filters smooth out the signal before it’s converted into digital data, reducing the chances of aliasing. Most professional audio equipment comes with built-in anti-aliasing filters, but you can also apply them in your DAW if needed.
The Science Behind Aliasing Sound
For those who want to dive even deeper, let’s explore the science behind aliasing. It all comes down to the Nyquist-Shannon Sampling Theorem, which states that to accurately reproduce a signal, the sampling rate must be at least twice the highest frequency in the signal. If this rule isn’t followed, aliasing occurs. It’s a fundamental principle in digital audio, and understanding it can help you avoid common pitfalls.
Why the Nyquist Theorem Matters
The Nyquist theorem isn’t just some theoretical concept – it’s a practical guideline that every audio engineer should know. By adhering to this rule, you ensure that your recordings are as accurate and clean as possible. It’s like having a blueprint for perfect audio production. Ignore it at your own risk!
Common Misconceptions About Aliasing
There are a few myths floating around about aliasing that we need to clear up. Some people think that aliasing only affects high-end audio equipment, but that’s not true. It can happen with any system if the sampling rate isn’t high enough. Others believe that aliasing is unavoidable, but as we’ve seen, there are plenty of ways to prevent it.
Debunking the Myths
Let’s tackle some of these misconceptions head-on:
- Myth: Aliasing only happens with cheap equipment.
- Fact: Aliasing can occur with any equipment if the settings aren’t right.
- Myth: Once aliasing happens, it can’t be fixed.
- Fact: While prevention is key, there are tools and techniques to minimize aliasing in post-production.
Tools and Techniques to Combat Aliasing
If you’re serious about eliminating aliasing from your audio, there are several tools and techniques you can use. From advanced software to simple tweaks in your workflow, here’s what you need to know:
Software Solutions
Many DAWs come equipped with built-in tools to combat aliasing. Look for features like oversampling, which increases the effective sampling rate, and anti-aliasing filters, which smooth out the signal. These tools can make a big difference in the quality of your audio.
Hardware Considerations
Your audio interface plays a crucial role in preventing aliasing. Invest in a high-quality interface with a robust anti-aliasing system. While it might cost a bit more upfront, it’ll save you time and frustration in the long run.
Real-World Examples of Aliasing
To better understand aliasing, let’s look at some real-world examples. Think about those old-school video games where the sound effects were a bit off. That’s often due to aliasing. Or consider a live concert where the high-pitched notes from a guitar solo sound distorted. Aliasing can happen in any situation where audio is being recorded or played back digitally.
Case Study: Fixing Aliasing in a Music Track
Let’s say you’re working on a music track and notice some aliasing in the high frequencies. Here’s what you can do:
- Check your sampling rate and increase it if necessary.
- Apply an anti-aliasing filter to smooth out the signal.
- Use EQ to remove any unwanted frequencies caused by aliasing.
With these steps, you can restore the clarity and professionalism of your track.
Conclusion: Mastering Aliasing Sound
Alright folks, that’s a wrap on our deep dive into aliasing sound. By now, you should have a solid understanding of what aliasing is, how it affects your audio, and how to prevent it. Remember, the key to great audio production is attention to detail. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting out, aliasing is something you need to be aware of.
So, what’s next? Take what you’ve learned and apply it to your own projects. Experiment with different sampling rates and filters to see how they affect your audio. And most importantly, keep listening – your ears are your greatest asset. If you found this article helpful, don’t forget to share it with your friends and colleagues. And hey, if you have any questions or comments, drop them below. We’d love to hear from you!
Now go out there and make some killer audio!
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Basics of Aliasing Sound
- What Causes Aliasing in Audio?
- How Does Aliasing Affect Your Audio?
- Recognizing Aliasing in Your Recordings
- Preventing Aliasing Sound
- Use a Higher Sampling Rate
- Apply Anti-Aliasing Filters
- The Science Behind Aliasing Sound
- Why the Nyquist Theorem Matters
- Common Misconceptions About Aliasing
- Debunking the Myths
- Tools and Techniques to Combat Aliasing
- Software Solutions
- Hardware Considerations
- Real-World Examples of Aliasing
- Case Study: Fixing Aliasing in a Music Track
- Seth Rollins Daughter Age A Deep Dive Into Family Life And Wwe Stardom
- What Happened To Bill Belichicks First Wife The Untold Story You Need To Know
aliasingsound LearnChemE
CS184/284A Lecture 3 Antialiasing
AntiAliasing Definition